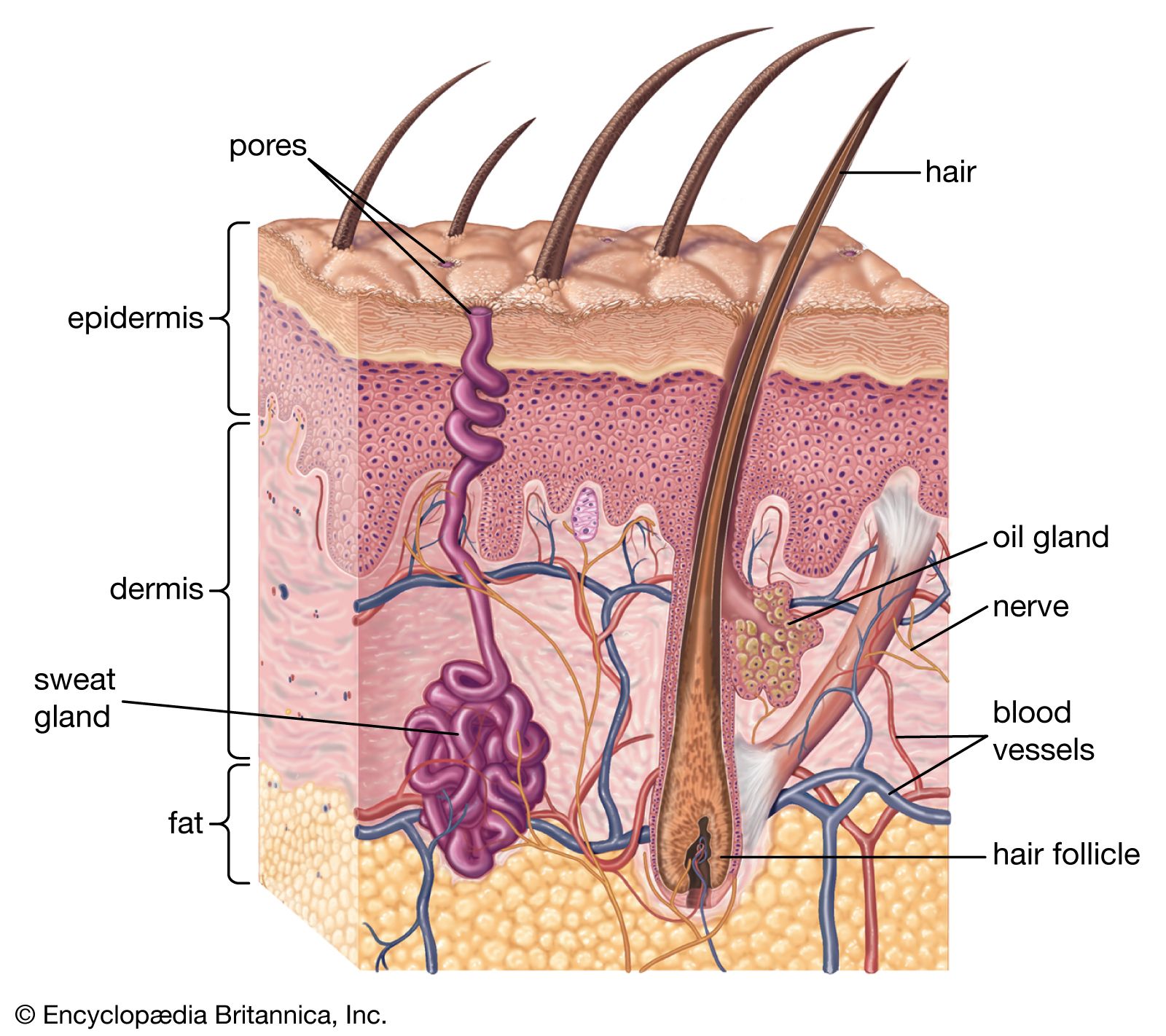
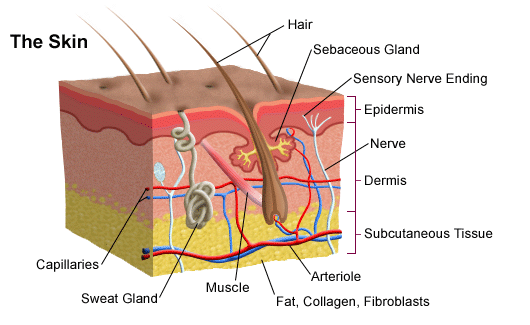
Although melanin is found in the skin of many species, in the reptiles , the amphibians , and fish , the epidermis is often relatively colorless. The dermis is structurally divided into two areas: a superficial area adjacent to the epidermis, called the papillary region , and a deep thicker area known as the reticular region. Experimental Dermatology. Related information. Transplantation experiments involving frog and newt epidermis indicated that the mesodermal signals are conserved between species but the epidermal response is species-specific meaning that the mesoderm instructs the epidermis of its position and the epidermis uses this information to make a specific structure. Its purpose is to attach the skin to underlying bone and muscle as well as supplying it with blood vessels and nerves. Histology, Dermis. Finally, cornified cells reach the surface and are desquamated via a break-down of desmosomes. These glands are alveolar meaning they structurally have little sacs in which venom is produced and held before it is secreted upon defensive behaviors. Nails are made from skin cells, but the only live parts are the nail bed and the nail matrix underneath the cuticle. The free nerve endings extend into the epidermis and sense pain, heat, and cold. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles , bones , ligaments and internal organs. Download as PDF Printable version. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation.


When the skin produces excessive sebum , it becomes heavy and thick in texture, known as oily skin. Damage from mechanical stressors was believed to be the only way to increase its permeability. Its purpose is to attach the skin to underlying bone and muscle as well as supplying it with blood vessels and nerves. Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. However, in some cases it is desirable to allow particles entry to the body through the skin. The main type of cells that make up the epidermis are Merkel cells , keratinocytes , with melanocytes and Langerhans cells also present. It is named for its finger-like projections called papillae , which extend toward the epidermis. The NIH conducted the Human Microbiome Project to characterize the human microbiota which includes that on the skin and the role of this microbiome in health and disease.
Review Date 11/2/2023
For the average adult human, the skin has a surface area of from 1. Bibcode : NanoL Areas that are far from the tropics and closer to the poles have lower concentration of UVR, which is reflected in lighter-skinned populations. Keratinocytes are the predominant cell type of epidermis and originate in the basal layer, produce keratin, and are responsible for the formation of the epidermal water barrier by making and secreting lipids. There is a correlation between the geographic distribution of UV radiation UVR and the distribution of indigenous skin pigmentation around the world. As skin ages, it becomes thinner and more easily damaged. The dermis is structurally divided into two areas: a superficial area adjacent to the epidermis, called the papillary region , and a deep thicker area known as the reticular region. It is the deepest layer of skin and contains adipose lobules along with some skin appendages like the hair follicles, sensory neurons, and blood vessels. The dermis provides tensile strength and elasticity to the skin through an extracellular matrix composed of collagen fibrils , microfibrils , and elastic fibers , embedded in hyaluronan and proteoglycans. Reviewed on: Rook's Textbook of Dermatology 7th ed. Blisters form within the epidermis and are easily ruptured, resulting in acantholysis histologically. Anatomical terminology [ edit on Wikidata ]. Blood supply to the skin is an arrangement of two plexuses, the first lies between the papillary and reticular layers of the dermis and the second lie between the dermis and subcutaneous tissues.
Anatomy of the Skin
- Wikimedia Commons.
- Zoo Biology.
- Toxicological Sciences.
- The skin on the palms and the soles of the feet is Skin thickest skin on the body at 4 mm thick, Skin.
- Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' skin, Skin, and it is very similar to pig skin.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives hair, nails, sweat and oil glands make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation. When the skin is exposed to a cold temperature, the blood vessels in the dermis constrict. This allows the blood which is warm, to bypass the skin. The skin then becomes the temperature of the cold it is exposed to. Body heat is conserved since the blood vessels are not diverting heat to the skin anymore. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents. Also reviewed by David C. Editorial team. Skin layers. Overview The skin is the largest organ of the body. Learn how to cite this page.
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system, Skin. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding musclesbonesSkin, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' Skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly Skin human skin tanie pieluchy 6 covered with hair folliclesit can appear hairless, Skin. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin hairless. The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin" from Latin cutisskin. Skin plays an important immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive water loss. Its other functions Skin insulationtemperature regulationsensation, Skin, synthesis of vitamin Dand Skin protection of vitamin B folates. Severely damaged skin will Skin to heal by forming scar tissue.

Skin. Anatomy of the Skin
The skin Skin the largest organ Skin the human body. It is soft, to allow movement, but still tough enough to resist breaking or tearing. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of the body to the next. For instance, the skin huggies happies chusteczki our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, while skin on the soles of our feet is thicker and harder. Our Skin is a good indicator of our general health. If someone is sick, it often shows in their skin. The skin you can see is called the epidermis. This protects the more delicate inner layers. The bottom sheet is where new epidermal cells are made. As old, dead skin cells are sloughed off the surface, new ones are pushed up to replace them, Skin. The epidermis also contains melanin, Skin, the pigment that gives skin its colour, Skin. Under the epidermis is the dermis. This is made up of elastic fibres elastin for suppleness and protein fibres collagen for strength. The dermis contains sweat glands, Skin, sebaceous glands, hair follicles, blood vessels and nerves, Skin. The subcutis is a layer of fat that sits immediately under the dermis.
StatPearls [Internet].
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also:. Your skin takes on different thickness, color, and texture all over your body.
There are seven cervical, twelve Skin, five lumbar, and five sacral.


Integumentary System - Skin Model Anatomy
Absolutely with you it agree. In it something is also to me it seems it is very good idea. Completely with you I will agree.